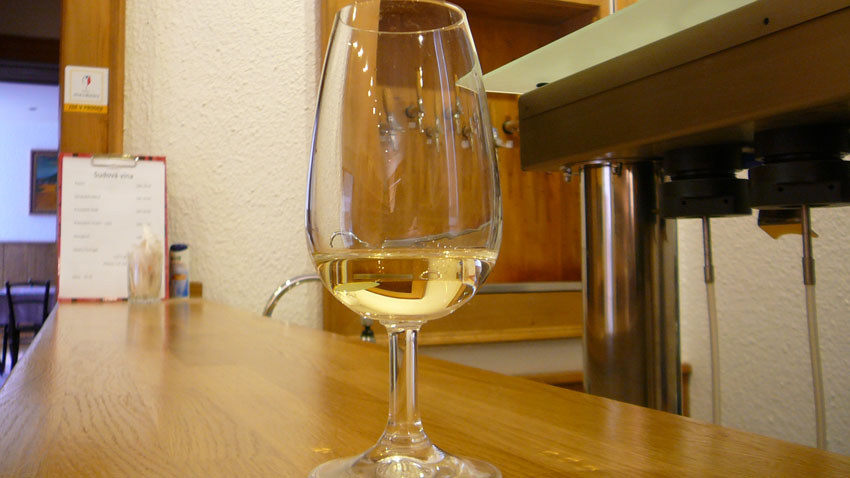
Vinotéka Stroh Hustopeče

-
Sales of quality Moravian wine.
The main domain of our wine is the promotion of small
Moravian winemakers, dedicating max. 10ha of vineyards.Vinotéka Hustopeče Stroh is focused on wines from small vintners and small Moravian and Moravian family of companies, which produce wine from Moravia and Moravian grapes. Our range of Moravian wines is complemented by gift packaging for wine, gifts, barman and sommelier needs and last but not least a lot of information about the grapes and the wine itself.
Wine Shop was created to offer you quality and interesting, many also unknown wines. We represent both wineries, which are on the Czech market for a long time and is known for its exclusive wines, and such wineries, not yet into the subconscious of many wine lovers entered, but their production is definitely worth trying.
Wines are immediately after transport from a vendor stored in our private wine cellar, where year-round optimal temperature and humidity. This is for you to guarantee the preservation of the characteristics of each wine for prolonged storage and eventual archiving older vintages.
Our customers but also other wine lovers regularly informed by mail (newsletter) news, future events or price reductions on our website. We have prepared an offer and tender packages, When we put together our experience packages and bottles, We have to fulfill your dreams of wine.
When you visit the wine cellar is sitting in a wine cellar and we prepared for cyclists sitting in the backyard.
Quality Moravian wines from many known and unknown winemakers
the wine region of Moravia and subregions Velkopavlovická,
Mikulovská and Slovácká.We offer quality Moravian wines, not normally
Available in retail.Vinotéka Stroh offer vína velkovýrobců, which you can find in any super and hypermarket. We offer you a comparable price, incomparably higher quality wines in small family Moravian winemakers.
How to choose the right wine
Experienced wine expert, If you want just to experiment, He reaches into his wine shop by mood, situation, or must be administered menu, after some of their favorite varieties from its proven vinaře.Následující lines, however, they are designed primarily for those, who to begin exploring the beauty of wine, and the right wine for himself, your family and your friends, still looking.
thousand people, thousand flavors. This old truth about our perception of food, doubly true for wine. Wine, that you advise your friend, as an excellent wine, can, but not, be good and best for you and vice versa.
How to choose?
1. According to the situation
Wine Shop by occasion, during which it will drink.If you want to donate wine, choose it accordingly, whom you want to donate. Board can be found in the section: Wine as a gift
2. Wine and food
So choose wine, so resonated with food, that you are going to serve him. Read rubric Sommelier advises. You can also use the menu divided by meals: Wine to cheese, Víno k masu, Wine for fish, Wine pasta, the vegetables and the sweet.
However, you can make decisions by other criteria:
1.by color
2.According to sugar content
3.Quality and attributes
4.by age
1. Wine Selection by color
The color determines its taste qualities. It is given in different ways processing of grapes. A detailed description of the flavor of wine can be found in the detail of each wine.White wine. White wines usually belong to the finer taste and uhlazenějším. They are particularly suitable for white meat, the fish and the sea, cheeses with white mold, the sliced cheese,…
Pink wine. Rosé wines abound mostly pleasant fruity taste. They are ideal for garden party, the pool, or for summer relaxation. Many of them recommend the vegetable, or pasta salads. You can even make them refreshing spritz. They can, of course, drink all year round.
Red wine. Red wines contain more tannin. Their taste is fuller and stronger than white, and rose wines. We recommend it with red meat, the freshwater fish, the dark cheeses and cheeses with a strong taste,…
2. Selection of wine by sugar content
Wines by the sugar content is divided into the following four groups:sweet – and they are marked with the sweetest wine. They 45 grams of sugar or more per liter.
Fortified – sweeter the wine center. Contain 12,1-45 g sugar per liter.
Polosuchá – medium-sweet wines with less sugar. Contain 4,1-12 g sugar per liter.
dry – wines with the lowest sugar content. no more than (simply said) 4 g cukru na litr.
Distribution of wines by the Wine Act of the Czech Republic
All fine wines grown in the Czech Republic are classified (divided and recorded). Classification process includes, inter alia sampling for the analysis of wines, its evaluation and archiving. The analysis carried out by an accredited laboratory. Inspections will decide, whether this wine can be disposed of and decide on its classification. Everything is documented by a written record. Classed wines are published on the website of the Ministry of Agriculture.Classification subject to the following wines:
- quality wine
- Quality wine with special attributes
- quality sparkling wine in specified regions
- aromatic sparkling wine specified region
- pěstitelský sects
- sparkling wine
- quality sparkling wine
Wine is divided into still wine and sparkling wine
Under Wine Wine MiStr.cz refer still wines, Therefore, most of the information in this section devoted to wines and soft information sparkling wines are just succinct. At the end of the article, however, find a link to the page with a detailed description of sparkling wines.Still wines – table wine
It is also the cheapest and lowest category of wines.Table wine must be made from grapes grown in any EU country.
Table wine may be labeled with the name “Country wine”, if it is, Besides, produced only from grapes of authorized varieties grown on the vineyard approved in the Czech Republic and the sugar content of the grapes reached at least 14 °.
Table or country wine is not subject to classification.
Still wines – quality wine
Quality wine may be produced only from local grapes harvested on vineyard approved, whose sugar content has reached at least 15 °. Its production must take place in the same region as the wine harvest. Classification of quality wines carried out by the Czech Agriculture and Food Inspection Authority. Quality wine can mark postscript “varietal” or “stamp”.Quality wine varietal not contain grapes, mash and cider from more than three varieties.
Quality brand wine must be made from more than three varieties of wine.
Still wines – Quality wine with special attributes
Quality wine with attribute všeškeré must meet the requirements for quality wines. The grapes must be from a single wine region, their origin, sugar, variety and weight validates the Czech Agriculture and food inspection. Wine can be made only from grapes, musts, or mash up to three varieties. Quality wines with special attributes are not preserved by chemicals, with the exception of sulfur dioxide.Quality wines with special attributes are further divided:
Kabinett wines. It is made from grapes, which reached at least 19 ° natural sugar content. Mostly it is a dry or semi-dry wine with a pleasant taste. We recommend consuming 1 – 3 years after harvest.Late harvest. The grapes for its production must be picked up at that time, the sugar content of grapes reaches at least 21 °. Most of these are quality wines, extract higher and lower to moderate sugar content.
Selection of grapes. Wine made from grapes, harvested after, What matured at least 24 ° sugar content. Often it is a wine with a higher alcohol content, extraktivní, polosuché nebo polosladké. It is suitable for archiving as a gift.
Selection of berries. The grapes for this wine aged for a very long time, to achieve sugar content of at least 27 °. They must be harvested by hand. This is a full, extractive wines with higher sugar content suitable for archiving as a gift.
Selection of raisins. The wine is allowed to be produced only from grapes affected by noble rot, or from overripe berries, which reached the sugar content 32 °. They must be harvested by hand. This is an exceptional, very full, extraktivní, mostly sweet wines.
Ice wine. The grapes are harvested by hand in the cold, at -7 ° C, or less, and must not defrost during pressing. Ice crystals that holds water and then there is molded. Sugar content bridge must reach at least 27 °. Ice wines are very extractive, They contain a lot of residual sugar and are relatively rare.
straw wine. hand-harvested, well seasoned and undamaged grapes are final drying for at least three months after harvest on straw or reed, or they are stored in a ventilated area. That is evaporated part of the water. They are mostly white grape varieties. Cider must have a sugar content of less than 27 °. Straw wines are, as well as ice wines, very extractive, They contain a lot of residual sugar and are relatively rare.
Still wines - dividing by the sugar content
Dry wine contains 0-4 g sugar / liter, or max. 9 g cukru/litr, assuming, that the difference between residual sugar and total acidity (when converted to tartaric acid) the maximum 2 gramsVíno polosuché obsahuje 4,1 – 12 g cukru/litr
Semisweet wine contains 12,1 – 45 g cukru/litr
Sweet Wine contains 45 g and more sugar / liter
Barrique
This is the oak barrels Content 225 l. From within the singed by fire. The wine matured in barriques barrels come from wood materials and thus affect its character. Depending on the degree burn barrel can then feel the smell of wood flavor, smoke, caramel, vanilla, but should also be chocolate or coffee ...With regard to it regarding to it, the barrique barrels can be used up to 3x, It is a complex production process. Thus mature wines because they have a special touch and is among the more expensive wines.
Wine of original certification
Wine of original certification, is also abbreviated VOC or V.O.C, They must meet the minimum quality requirements for quality wine and must be produced on a smaller area, than the wine region. His producer must be a member of the association, which is authorized to grant the designation of wine of original certification. Although this wine is subject to supervision, but it is not classified as, As with quality wines.
sparkling wines (fined)
Sparkling wine is produced by fermentation of the grapes, or must, or wine, If these are suitable for the production of table wine.Distribution of sparkling wines according to quality:
- Quality sparkling wine - champagne.
- Quality sparkling wine in specified regions – sekt s.o.
- floricultural sparkling wine.
- Aromatic sparkling wine.
- Quality aromatic sparkling wine in specified regions – aromatic champagne s.o.
Distribution of sparkling wine by sugar content:
- Brut nature – naturally hard. It contains less than 3 g cukru/litr, After secondary fermentation must be delivered no sugar
- extra brut – particularly hard. contains the 0 a 6 g cukru/litr
- Brut - tvrdé. It contains less than 15 g cukru/litr
- Extra dry – especially dry. contains 12 – 20 g cukru/litr
- Sec - dry. contains 17 – 35 g cukru/litr
- Demi-sec - polosuché. contains 33 – 50 g cukru/litr
- Sweet - sladké. It contains more than 50 grams of sugar / liter
Sparkling wines are classified according to quality:
- sparkling wine
- Sparkling wine
Liqueur wines are classified according to quality:
- liqueur wine
- Quality sparkling wine
More information about sparkling, sparkling wines and liqueur can be found can be found on the national website of the Czech and Moravian wines.
Distribution of wines by age- Young wine
- mature wine
- vintage wine
Distribution of wines by the senses
- Color – whites, pink, red
- Scent – fragrant, neutral, malodorous
- Taste – dry to sweet, empty to full, dull to acidic,…
Wine – the types and distribution
Wine is alcoholic and nonalcoholic beverage typically arising fermentation of musts from fruit grapevine. The word wine comes from the Latin vinum.
by color:
White wine: Made from white, pink, red, or blue grapes. During its production, the mash (damaged skins of grapes) immediately compressing and recovering the pure juice Fermentation. Solid residues after pressing are called marc. White wines made from red or black grapes is called claret.
Pink wine: Made from red grapes without fermentation, For table sparkling wines and sparkling wines and from a mixture of white and red wine.
Red wine: Only made from blue grapes (because the red dye is only in these varieties), and nakvášením or thermal treatment. During its production, the mash was allowed to ferment for several days. Husk and remain in contact with the fermenting juice. Fermentation takes time and at higher temperatures than white wine. In red wine they are thus at a higher rate and also tannins drug substance resveratrol (peel and seed from), which is found in white wine. The two-ounce glass of red wine contains 600 micrograms of resveratrol. Recent research allow to produce red wines with up to 3x higher content of resveratrol after irradiation during ripening.
According to sugar content:For wines:
- dry: maximum 4 g residual sugar / liter
- polosuché: 4,1-12 g of residual sugar / liter
- semisweet: 12,1-45 g of residual sugar / liter
- sweet: minimum content 45 g residual sugar / liter
The sector:
- “brut nature” “naturally hard”: less than 3 g sugar / liter (Sugar has not delivered)
- “extra brut” “particularly hard”: 0-8 g sugar / liter
- “brut” “hard”: sugar content of less than 15 g sugar / liter
- “extra Dry” (“extra dry”) “especially dry”: 12-20 g sugar / liter
- “sec” “dry”: 17-35 g sugar / lit
- “demi-sec” “polosuché”: 33-50 g of sugar / liter
- “soft” “sweet”: over 50 g sugar / liter
According to the class and type
table wine: table wine made from grapes harvested in the Czech Republic, which reached at least 11 degrees sugar content (grapes with sugar content 10 degrees can be processed by special permission of the Ministry), or mash, musts and wines obtained from grapes of wine grape varieties and registered as a table - and imports. The process can also be used unregistered varieties of grapes planted in front 1. 9. 1995. Table wine must not be called varietal name or the name of a wine region.
quality wine: They produced from grapes harvested grape varieties in wine regions of the Czech Republic, which reached at least 15 degrees sugar content, or possibly the mash must from these grapes. It is produced in two varieties. Quality wine is in addition to the basic data marked with the name of a wine region, in which the grapes were harvested for the production of, and the name of the variety, from which it was made.
- Variety wine must contain at least 85 % wine produced from the variety indicated on the packaging.
- Label wine may be produced by blending high quality varietal wines.
Wine with special attributes: produced from grapes, mash or must one grape vine varieties[source?] wine region set for implementing regulation, harvested in the vineyard tracts. Wine with attribute must contain at least 85 % wine produced from the variety indicated on the packaging. Wine with attribute is additionally known name attribute, name wine regions and wine villages and the year of the grape harvest.
- Kabinet: produced from grapes, which reached at least 19 degrees of natural sugar content.
- Late harvest: produced from grapes, which reached at least 21 degrees of natural sugar content.
- Selection of grapes: produced from grapes, which reached at least 24 degrees of natural sugar content.
- Selection of berries: produced from grapes, which reached at least 27 degrees of natural sugar content.
- Selection of raisins: produced from grapes, which reached at least 31 degrees of natural sugar content[source?]
- Ice wine: produced from grapes, harvested at temperatures of minus 7 And lower C, during harvesting and processing
They remained frozen and the obtained must exhibit at least 27 degrees of natural sugar content. - straw wine: produced from grapes, which have been stored before processing on straw or reed or hung in a ventilated
space for at least 3 months and the obtained must exhibit at least 27 degrees of natural sugar content. - botrytis cinerea selection: They produced from grapes affected by noble rot.
- Barrique: the wine is aged in oak barrels and partially reproduces the scent
- on binds: wine in the containers located on the fine yeast, which are shuffled
natural wine: Natural wine is considered to, which is not chemically treated.
sacramental wine: mass wine is especially closely monitored natural wine, which is not chemically treated or in the growth and maturation, nor used any chemicals or additives in its production and throughout the growth and production monitored in charge of the spiritual church. In the past, the sacramental wine produced mainly in monasteries only for the purpose of the Mass, as transubstantiation wine for the Blood of Christ – Eucharistii.kosher wine: in the case of kosher wine is necessary that the technological process for the duration supervised by the representatives of the Jewish community.
flavored wine: produced from wine or grape must (and mixtures thereof), with addition of water not more than 15 %. Aromatized with natural aromatic substances or permitted aromatic extracts, aromatic herbs and spices. It is also possible to use additives authorized flavoring substances. The sweetening sucrose is used, grape must or concentrated grape must. The doalkoholizování is used as a natural alcohol, that the actual alcohol content in the final product to reach at least 14,5 % and up 22 % volume.
- Vermouth: designation is used in case, that aromatization was conducted flavoring substances derived from wormwood and sweetening was performed only caramelized sugar, sacharózou, grape must or concentrated grape must.
- American: the bitter flavored wine exhibiting a characteristic bitter taste. The flavorings are used natural substances from wormwood and gentian. Yellow or red color is obtained by using additives permitted.
liqueur wine: must have at least 15 % volume and maximum 22 % volume of actual alcoholic strength and the least 17,5 % vol total alcoholic.
- Quality sparkling wine produced from grape must, of wine or a mixture of grape must and wine, It can also be produced from wine distillate.
- Liqueur wine wine production area - see above, cider and wine used must come from wine-growing regions and registered varieties.
dealcoholized wine: It manufactured from common grape varieties such as. Merlot, Riesling, Müller Thurgau, Dale je Vermouth Rosso Bitter, Rosé a sekt. It is not a grape, as is often mistakenly assumed. The foundation is the classic wine, from which subsequently such. Ethanol was removed by vacuum technology. Dealko wine must be less than 0,5 % alcohol. They are fuller and more aromatic varieties, since the dealcoholization process removes up to about 20 % taste the wine itself. The amount of residual sugar is u Müller Thurgau ca. 2,5 g sugar / liter, u Riesling, Rose and Merlot between 20-50 g sugar / liter.
sparkling wine: produced from domestic table wine or quality carbonation, must have at least 9 % total volume and alcohol content of at least 7 % vol actual alcoholic strength; overpressure in the bottle at 20 ° C must be in the range 0,1 when 0,25 MPa. Wines thus treated are crisp and well drinkable. In comparison with effervescent wines such wines sparkle is smaller.
Sparkling wine: It is the kind of wine, wherein the dissolved carbon dioxide, produced during fermentation, the sugar is converted into alcohol and carbon dioxide. In the production of other wines freely carbon dioxide escapes, in the production of sparkling wines, this is prevented by, the wine ferments during the secondary fermentation in a closed bottle. A second method is the production of sparkling wines in closed tanks.
- Sparkling wine: It is produced by primary or secondary fermentation of wine. The total alcoholic cuvée used in the manufacture must be at least 8,5 % by volume and the pressure in the cylinder at 20 C for at least 0,3 MPa, this kind can not be described as sects.
Sparkling wine is among the basic data referred to as a type of wine, place name, which was carried wine production. - Quality sparkling wine (fined): produced by primary or secondary fermentation of musts and wines (and imports) of varieties, which are permitted in the country of origin for quality wine. The overpressure in the bottle at 20 ° C must have at least the classic bottle 0,35 MP, the total time of production during fermentation in tanks must be at least 120 days in the period 1. January 2002, the total time of production during fermentation in bottles must be at least 9 months. fermentation time (from the beginning of fermentation to drain) in tanks without mixing device must be at least 60 days, using a mixing device at least 30 days. The total alcoholic cuvée used in the manufacture must be at least 9 % volume; using cuvée least one variety 8,5 % volume, the actual content of alcohol in the finished product must be at least 10 % volume.
- aromatic sparkling wine: An aromatic sects can mark aromatic sparkling wine, if during its manufacture using only a primary fermentation of musts cuvée only varieties Irsai Oliver, Moravian Muscat, Muscat Ottonel, Traminer and Müller Thurgau. It must also be met in other technological requirements imposed by law. labeling: Aromatic sparkling wine in addition to the above data indicates the name of one or indication, the wine was produced from aromatic varieties of grape.
- Quality sparkling wine wine region (champagne wine region): It produces a secondary fermentation cuvée of quality varietal wines, wine regions, and just inside the wine region, in which the grapes were harvested for the production of. The overpressure in the bottle at 20 C must be at least 0,35 MPa, with the exception of bottles in volume 0,25 lt. The total production time including the aging must be at least 180 days during fermentation in tanks and 270 days of fermentation in bottles. The fermentation time must be at least 90 days; fermentation in tanks, using a mixing device at least 30 days. The total alcoholic cuvée used in the manufacture must be at least 9 % volume; using cuvée least one variety 8,5 % volume, the actual content of alcohol in the finished product is at least 10 % volume. Sparkling wine is among the basic data referred to as a wine region, in which the grapes were harvested.
- floricultural sparkling wine: is manufactured, if the conditions of the production of sparkling wine region with, the actual production will take place at the vine growers, whose grapes were used to make.
Production of white wines
The grapes are crushed and the resulting mash is pumped directly into presses or without draining containers, in order to drain relaxed cider, so. samotok, and increase the use of presses. When processing the grapes of stem with unripe grapes is recommended ginned, their tannins being walked upon pressing into cider and could adversely affect wine quality. The pulp remaining after the sieving must be pressed and the must is pumped into the fermentation tanks. When processing unripe or rotten grape juice before fermentation elutriated, to get rid of unwanted sludge substances, or. deacidified, if it contains a higher content of kyselin.Rmut healthy ripe grapes aromatic varieties with leaves 1-2 hodiny macerovat, to peel grapes must release to the most aromatic substance.
Mash remaining after sieving must be compressed to various types of presses.
Cider from insufficiently ripe grapes, achieving a sugar content of less than 19 °NM, must before fermentation is adjusted by adding beet sugar (may only be used in the production of table wines and quality, rather than quality wine with special attributes).
Fermentation starts spontaneously either (spontaneously) activities already contained in yeast must, or it must zakvašuje bred pure culture yeast. These ensure fast fermenting cider, improved fermentation of the sugars contained in the must and fermentation cleaner, because the faster formation of ethanol prevents the reproduction of unwanted organisms. Optimum conditions for fermentation yeast concentration is sufficient, their good health, temperature 13-18 °C, needed oxygen for breeding yeast, the necessary concentration of sugar and acidic medium having a pH 3,5-4. Fermentation was carried out so quickly and cleanly, it is a need, so must not be too cold and contained enough oxygen necessary for the rapid development of yeast.
Because high temperature weakens the vital functions of yeast, and the impact of both on fermentation průběch, and quality wine produced, must avoid excessive increases in temperature during fermentation.
This is achieved by lowering the temperature by slowing the fermenting must and fermentation. With a reduced activity of yeast is reduced and the amount of heat generated by yeast.
Production of red wines
In the production of red wines ginned mash is fermented in open or closed containers, to release the dye stored in plastids (Solid bushes in tanning) unpeeled berries. Due to the increasing content of alcohol in fermenting mash these plastids become brittle and crack, and the dye is released from them. Release of dye from plastid disrupted mechanically accelerates mixing and fermenting the mash formed by dipping grape marc hat. After completion of the fermentation the mash is pressed and molded the young red wine is pumped into the storage cellar, The treatment as a young white wine. At the ripe grapes may be used so. karbonickou maceraci.
Blue grapes is necessary in the production of red wines odzrňovat, It would mash fermentation moved into the new wine and the tannins contained in třapinách. The temperature during fermentation mash must be checked, because at higher temperatures, loses color and there is also a risk of infection acetic bacteria. Method and fermentation time depends on the ripeness and color characteristics of the grapes as well as by the different varieties. The longer it takes fermenting mash, the more young wine contains tannins.
In the production of red wines is also used so-called. fermentation over four. In this method, at the beginning of fermentation mash is added in sufficient red wine, that the alcohol content in the mash is raised to 4 obj. %. Elevated alcohol content is already at the beginning of fermentation accelerates release of red dye and suppresses the development of undesirable microorganisms. This method of production of red wines is also used to improve the quality of older red wines.
Release of dye from the skins of red grapes are also achieved so. warm way. when heated mash gently pressed screw presses. At temperatures 60-65 C is heated mash 1,5 when 2 clock, at 70 For thirty minutes and at temperatures 80-85 C two to three minutes.
Then prokvašuje only must the color obtained in the same manner, as is the fermentation of white musts. The produced red wines have a high saturated color, but the taste is slightly different from the red wine, produced by conventional fermentation of mashes.
Because the rotten grapes are damaged blue dye, it is better to mash nekvasit, ale vylisovat done na.
And maturing wine bottling
Carefully treated wine barrel after reaching maturity ready for bottling. Appropriate technological interventions can be for their fine wines aging in bottles slow, so that it can retain the full quality and many years. Development of wine while lying in bottles but not at all the same wines. While the wines with higher concentrations of extractive substances and alcohol may leave the bottle on a longer time, wines made from lower-quality grapes reach their peak of quality in a relatively short time, and they are therefore not suitable for long-term storage. To determine the suitability of a particular wine for longer storage is necessary to know the details of the wine – its origin, vintage, extract content, acids, etc.. You can give us other than the manufacturer by an expert and experienced wine shop worker, which is sold with wines perfectly acquainted.
From the first float stáčeček with a capacity of several dozen bottles of shift soon passed (even before World War II) stáčečkám the capacity Corresponding size plants, which at that time was not too big.
The increasing capacity of filling machines, which adjusts production program, builds capacity bottle washers, zátkovaček, etikatovaček and packaging machines, which are part of the bottling line. From a business perspective, the bottles and packaging, ie. quality plugs, artistic side of labels and packaging method, a very important business factor.
[/spoiler]
[spoiler title=”Wine production – description” style=”fancy”]Wine production – DESCRIPTION
picking grapes
The basic raw material for the production of wine is fresh grape vine. Harvesting of the grapes takes place on our vineyards since the end of August (u early varieties) around the end of November(late varieties). The quality of the grapes at the time of harvest the maximum potential of wine, which of them can be made. Then it depends on each winemakers, As part of this potential can be transferred into wine. Using today's technology can be anywhere, which they are grown quality grapes, also produce quality wine. If this is not done, this is usually due to a combination of excess production yields and imperfect, the wrong technology and equipment or lack of knowledge, or both.
ginned
Another important step is the harvest of stem separation from berries. This process must also be carried out very carefully, because in case of violation of seed berry they would get into the wine unwanted bitter substances and the production process was already in his early spoiled. Such modified berries with more or less distorted peel is called mash.
stamping
The mash is then pressed. For red wine mash the leaves prokvášet days 7-10 with lighter wines to 30 days with heavier fuller wines. During fermentation, the wine releases tannins from the skins and dyes. The optimum temperature of this process is about 29 degrees. For maximum extraction of color pigments must be called. mash hat still immersed in the must. For white wines, the mash is pressed almost immediately, But a few hours also keeps in contact with skins, to the must releasing more aromatics.
Fermentation (fermentation)
Is biochemický process, in which the grape sugar through yeast and enzymes becomes alcohol and carbon dioxide. Chemical formula of this process is the: C6H12O6 = 2 C2H5OH + 2 Sugar Alcohol CO2 = + Carbon dioxide + teploTeplo and carbon dioxide escapes into space. process ustává, when sugar stocks run out or when the alcohol level reaches grade, which is toxic to yeast enzymes. Or fermentation can be stopped artificially, using several different methods: heat, sulfur dioxide, centrifugal filtration, alcohol, pressure or carbon dioxide.
malo – lactic fermentation
Is biochemický process, wherein changing the malic acid to lactic acid and carbon dioxide. It is therefore done, to alter the sharp taste of malic acid to softer taste of lactic acid. It is mainly used in the production of red wines and Fuller, richer and more complex white wines. To make the fermentation took place, requires the presence of lactic acid bacteria. They are naturally found on the grape peels together with the yeast and other microorganisms or added to wine. To fulfill its tasks need an environment with a temperature, low sulfur content, ph factor 3-4 and nutrient supply of grapes.
training wine
The next phase of wine making his training. It is called as a set of operations, which performs cellarman from pressing to bottling wine, and aimed at improving the quality of. They are particularly: clarification (fining)It is one of the technological processes, in which the fining agents by means of various natural impurities found in wine pressed down (sedimentace) container. When stáční wines remain dirt and unwanted substances in the container and are subsequently removed. Principle clustering around clarifier impurities of opposite electrical charge of particles. For this purpose, for example, negatively charged bentonite, tannin also negative, gelatin and whipped egg whites with a positive charge, etc.. filtration
Wine is a process whose aim is to rid the wine solid parts. It is an operation, in which particles are separated from the wine turbidity at a flow of a porous layer of filter material. In the basement of the economy are two types of filtration alluvial, When the metal meshes alluvium filtration material (mostly diatomaceous earth) through them and then filtered wine, second type filtration plate, when the wine is filtered over cellulose plates
For some great red wines is to perform is bottled without clarification. Consumers should be advised to, that during maturation will be at the bottom of the bottle to form deposits. Filtering is done using filters for wine. The principle is flowing wine over a hurdle (filter) which captures the solid parts contained in wine. Sharpness filter is proportional to the size of the filter holes.
bottling
Equipment for bottling varies by company size. Even smaller winemakers often use manual filling. The bottles are filled one after the other and then zátkují hand zátkovačkou. Some of the larger companies outsource these jobs, to them specialize. They usually have good equipment and work carried out perfectly. Another option is to own bottling line, this requires considerable additional investment.Really there is someone, who needs advice, How to taste wine? Yet just raise a glass, drink, polknout a – If everything is alright – sense of taste?
therefore, ano and not. Simple sipping small sips, or even large gulps mean, that wine sufficiently relish. Just in case, if the wine require simple refreshment, or if, co drink, liter bottle of cheaper table wines. But if you drink wine because, that you particularly like and you find, that adds a new dimension to eat, then you realize, the wine is different from other beverages. The taste and behavior is generally more comprehensive and the best wines have the ability to accurately reflect the origin and age to improve.
Faced with this potentially charming fluid makes sense to provide maximum enjoy every sip, glass and bottle. This means tasting, not just drinking. On the other hand, it is not necessary to resort to all those grimasám, Sipping a recording impressions, typical professional taster, whose livelihood depends on an accurate assessment of the quality, aging potential and commercial possibilities of wine. Suffice sophisticated drink – golden mean between mindless drinking “the former” professional and objective approach. And everyone can. It just takes practice – the more, the better – and efforts to remember and re-equip the smells and tastes. find, that writing notes – tasting especially if more than one wine – significantly accelerate the learning process.
You need for social tasting room odorless, with an acceptable intensity of illumination, and simple equipment – mostly clear, odorless glasses, for each of at least one large enough, Tulip undecorated glass with foot. If you use a glass for tasting more samples, before going from white to red wine, it thoroughly with water and pour into it a little bit new wine, swirl and pour contents.
You will also need some light background, For example, white paper, white cloth or sheet, against which you will assess the appearance of wine. The spitting of sampled obtain a sample bucket, bowl or mugs or use a nearby sink. Prepare water and bread, to get rid of the previous wine taste in the mouth. Get the tools to cool the white and sparkling wines and aluminum foil to cover the label, To make an anonymous tasting. Those přičinlivější forget the pen and paper for taking notes.
Appearance of wine you can tell a lot or almost nothing – It depends on wine. However, you should be there at least briefly stop. If nothing else, at least find, whether the glass pieces swim corks. While this is not serious, nor nothing pleasant, when you get into your mouth.
Čirost – Wine in good condition should be pretty clear, unquenched and not fogged. Bottles cloudy, Moke corrupt today fortunately rarely find themselves in the retail network and a single přičichnutí and tasting should confirm, that something is wrong. The cause of the cloudy appearance is likely sediment (deposits dye, tannins and tartrates), Blowing handling bottles. This is more commonly found in red wines.
Given the current trend towards the abandonment of intensive filtration (In some cases, the wine is not filtered at all even) Today, we see plenty of wines sedlinkou. And it does not always go the old wine. The sediment can start to create a good two years in the Australian blend of Cabernet Sauvignon and Shiraz. Taste and texture can be quite dirty, so if you suspect, that the bottle may be sediment, Carefully pour the wine and never Never spill bottle to the dregs (Allow at least inside centimeter high residue). Sometimes on the label, the wine is unfiltered or that it could create grounds.
For white wines are more likely, that you see at the bottom of a glass of colorless crystals or just below the surface of the wine bubbles. Crystals produces harmless tartar, which demonstrates – like sediment – that wine was not overly trained. The young wines can be found harmless carbon dioxide bubbles, that the tongue lightly bites. Bubbles will also have any red or white wine beginning to ferment (becoming bitter). In this case always be accompanied by a must-acetic aftertaste.
Color – the color of the wine speaks of his age, origin, the variety used, method of fermentation and maturation, and by extension, the quality. White wines that reveal themselves generally less than red, however, their color ranges from almost translucent, sometimes a tiny greenish tinge, After a deep golden and darker shades. One key factor is age. White wines darken with age until brownish color, which – with the exception of wines dolihovaných, very Madeira – testifies, the wine is long past his prime.
The color also affects the origin of the wine. In the increasingly colder conditions ripened grapes, this is paler wine, has a higher acidity and its color will darken slower. Reverse is also true – the warmer climate, the wine has a yellower color, a lower acid content, and will age faster. However, there are some exceptions. Grapes affected by noble rot wine, a bolder colors.
The color of white wines can also darken the fermentation and maturation in oak barrels. But to make it even more difficult, White wines fermenting in oak barrels are often aged in barrels on lees (dead yeast), preventing them from yellowing. Color is important rather red wines. Where white wine darkens with age, Red fades and loses color in the form of sediment. Like the white and red wines gradually turn brown. To znamená, the rich, purple-red young wines gradually subsides ruby, garnet or brick, and finally passes into a faded umber tint, which indicates, Wine that has optimum ripeness behind. The more mature red wine, the greater the gradation of color from the – darkest parts – the lightest outskirts. In the old fluid is almost colorless edge. Red wines aged in wooden casks for a long time additionally lose more than the color of wine lying mainly on the bottle.
As with white wines and red wines true, that the warmer climate, the darker the color. this explains, why so many dark red wines, ink shade.
Viscosity – Initial swirled the wine in the glass that although you will not gain much, but wine, at which flow along the walls produces a distinct viscous “legs” whose “tears”, probably has a fairly high content of the alcohol or sweet. Wine, in which the edge of falling apart if, instead ran out in those tears, is probably quite old, or light and dry.
From the smell, you can learn more about wine than the appearance or taste, But the mere insertion of the nose to the glass enough.
When the glass spurts a familiar scent – gooseberry and blackcurrant, you suddenly feel, that you understand the whole tasting. But it is equally possible, that you can not immediately identify any specific scent – and certainly not the flood of exotic fruits, flowers and vegetables, It is some tasters seem to always be able to recognize. Instead, find, even after the second glass of wine swirled smells nu, again only for wine, and certainly not after the grapes.
Revealed fragrance – Only a handful of wines – mainly those made from muscat varieties – actually smells like freshly torn grapes. Ability to recognize the scent, you feel, it is a question of practice. In this case it is no accident, but some of the wines in this respect are undoubtedly easier. For example, hardly missed a lush varietal aromas of Traminer – lychee, face cream and Turkish delight. In cooler climatic conditions generally arise wine with subdued aromas, whereas with advancing age in the wine bouquet develops complex substance, which are harder to detect.
Try to use our broad prompter list (preparing), helping you identify aromas in wine. This list is not official or final, so to him at will attach to other categories.
Whatever you do while, trust your senses. Do not get trapped into a trap of an effort to differentiate all of the flavoring substance and bouquet, because you think, that in this wine should be present. Always follow whichever you feel all alone. Just so do not be afraid, that your words will sound snobbish. Wines can really smell of green pepper, roses, raspberries, pears, bananas, mown grass, vegetables and common materials, because the grapes will find many of the same chemical compounds. For example methoxypyrazine give wine aroma of green peppers, which so often discover the Cabernet Sauvignon, and gooseberry and pickled asparagus, which reveal some Sauvignon. But it would be pointless – nay snobbish – declare: “Mmm, This claret feel distinct methoxypyrazin.”
sources fragrance – Determining the individual aroma components is satisfactory and beneficial, but it is only one aspect of the sensory evaluation of wines. The aim is not to compile a description reminiscent shopping list, but check, both aromatic and bouquet substances intertwined, and create a picture of the character style (including age) and the quality of the wine. So you know, not only what you love, but also why and – especially – what else you could appeal to.
When you learn to know the style of wine, remember, that aromatic substances derived from three main sources or phase. First – so-called primary aromatics, often apparently fruit, flower or vegetable – They come directly from the grape variety. In contrast, secondary aromatic substances formed during manufacture. For example, the smell of butter or cream can be found especially in white wines, which have undergone malo-lactic fermentation. scent of vanilla, wood shavings and toast are associated with the use of the new oak barrel during the fermentation process or maturation. A number of wines is beyond these two phases never get. They are intended for early consumption and aging do not get the quality.
older wines – The third group – tertiary aromatics, often the most difficult definable – they are complex, mature component, which develop during the maturation of high quality wine in the bottle. Fresh fruity aromas of fresh crushed grapes gradually replace the intertwined layers of heavier scents. Although wine does not smell so much fresh and lively as a young mok, but still it's the smell should be clean, not stale and tired.
In white wines are among the conspicuous tertiary aromatic substances honey (in both dry and sweet wines), toasty, roasted nuts and kerosene. In red wines with aromas of fruit, while refines, but somehow zesládne and “zpodzimní”. Sometimes you recognize hints of dried fruit or potpourri and often spicy venison tones and shades of leather. At this stage begins with a professional taster often talk about “buketu” fault.
These scents can be quite profound, sometimes repulsively. In this case, you come across a wine or style, that will not fit. Some consumers feel kerosene aroma of fine Riesling Old unexpected and unappetizing. Others are shocked at the first whiff of a barn or stable in mature red Burgundy. Some of the old red wines, especially red Bordeaux, may emit odor reminiscent fungi. None of these fragrances should prevail, but as part of a multi-layered bouquet of wine can add aromatic attractive shades. Surprising, however, odors are not just the domain of old wines – aroma Sauvignon and Müller Thurgau were compared to a feline or spray Kocicin. If you happen to come across a fragrance, that makes you, People told, “fall ass”, but that you think nothing about spoiled wine, consider her soul mate one of those horribly smelly, but delicious French cheeses.
The intensity of fragrance – Once you get the idea, After what wine smells and whether it is likely to be young, old, or somewhere in the middle, Think Odor Intensity. is pronikavě, luxuriant, refined, restrained, or almost imperceptible? If too dim, There are three options – Wine can be made from at least one aromatic varieties, or it can be a cheap ordinary wine varieties, which are not regulated revenue and grapes that give very watery taste. Another alternative is, that you hold in your hands a quality wine, but it is not yet ready for consumption and passing the so-called silent phase. Sometimes you can revive such wine, when steep glass and shake hands with her (maybe you'd better try first with water). Often just they need more time to lie on the bottle, maybe a few months, or even years, To “peeled away”. If you purchased the wine from several bottles, resist the temptation to be patient.
Let it sounds strange in any way, Your taste buds will tell about wine less than smell. Upit sip however amplify and specify the acquired impressions.
If the wine feel, well you can not even determine its taste. It can try a simple test: zacpěte if we. That does not mean, that would taste like sensory organs redundant. Your taste buds play a decisive role in assessing the impression of fullness and structure of the wine and the main non-volatile substances. To my taste buds compelled to work, you have to give a swig and then his tongue poválet. At this stage, you can either swallow wine, spit, or resort to further the optional custom professional tasters. Gently open your mouth and pulled in a little air. If you think, it sounds scary, so wait, until you get to spitting. The intention is to aerate the wine and the volatile component to push the back of the mouth to the front tip of the olfactory lobe, where the olfactory nerves transmit impressions to the brain. after tasting, “analyzing the” and swallowing or spitting, consider, how much and what aspects still taste in the mouth. Length mouthfeel and its impact or aftertaste, “tail” etc. They are key indicators of the quality of wines. The longer and more enjoyable, the better the wine. try to calculate, how many seconds last.
Solids
Your first impression of taste is likely to confirm a large part of the, what you found in the aroma, because the same flavor substance was moved to the back of your mouth to the carina of the olfactory lobe. But probably find, the relative intensity of various aromatic substances changed, as you are now experiencing, together with the taste and texture components. One of your main goals at this stage is to find out, that all components of the wine in balance.
Taste buds are sensitive to four basic sensations – sweetness, acidity, bitterness and saltiness (although that in no way are not many wine). Many people perceive the most sweetness on the tip of tongue, acidity and bitterness sides, which caused some tannins in red wines, in the back of the tongue. This model, however, is by no means universal, therefore rely on him, If you are unsure, that he reply.
Acidity
Begin assessment, as sour and sweet wines and that both these properties in balance. Acidity is a necessary part especially sweet wines; if they are missing, can be horribly repellent. In dry wines, you can make out a small amount of residual sugar, So sugar from grapes, which is not enough to convert the alcohol. Impression of sweetness can also cause taste ripe fruit, alkohol a glycerol (byproduct of the fermentation process). Remember, the wines from warmer climatic conditions are generally more mature fruity flavor and higher alcohol content and glycerol than those coming from colder zones. Therefore, the dry wines from the New World may seem “sweeter” than wines from the Old World, made of the same varieties. Higher alcohol content of glycerol also gives a fuller wines smoother, sometimes a little oily texture.
Acidity, which is higher in colder conditions, especially white wines gives the necessary vigor and zest. If it is not, however, fruitiness and alcohol, just taste wine sour. In the warmer Australian climate acid is added to most white wines artificially, that was harmoničtější. But not always winemakers achieve the right balance, and sometimes – instead of adding wine liveliness and briskness – neprolne acid with other components of wine.
service life
Acidity is also a major cause of long-life white wine, with the aging gradually softens. Young white wine for the archive to be beginning to need a fairly high degree of acidity. The oak barrel wine prokvášející, which excel new dimension of flavor and rich texture, you will not feel so much like sour wine, that in them Nekvasil. It is not easy to judge, whether the balance of acids in white wine intended for proper maturation. The most important is a sufficient amount of fruitiness, that the time, before acidity perfectly soften, nezeslábne. The ideal ratio is largely a matter of experience – for the taste buds, while welcoming, but no less tooth enamel.
tannins
Acidity is also important for red wines, But there are more indispensable tannins, especially in red wines suitable for storage in the archive. These substances are astringent effect also present in tea. It can be detected by taste buds sensitive to bitterness. In parallel with the aging of wine with tannins soften, but in some very young, high quality red wines can be uncomfortably intense. When tasting wine, try to assess, tannins that are too hard and rough, or if behind them recognize the depth of ripe fruit – sufficient to, to tannins withstood.
Currently, worldwide wines produced from grapes more mature and more mature tannins, and therefore they are fruitier and more accessible now at a younger age. At the same time, however, lead the trend even bigger, still more concentrated red wines. This may lead to, the winemakers – in an attempt to squeeze out of the blue grapes every last drop of flavor – of them also extract too much tannin. Until someone is able to control climate, They will always be in cold climates weak volumes, which will arise barely ripe grapes with hard, immature tannins.
On the opposite end of the scale are silky and smooth wine (imparts smoothness glycerol). This may sound tempting, but too fine wine lack tannins or acids, may seem dull and flabby. Before the first glass drink, you will probably find it boring taste a wine will have no potential of ripening.
Dub
Another potential source of imbalance oak aroma. Dubenky already capture the scent, but it better reveals the taste. Assuming, by carefully using, the right kind of oak (new or nearly new barrels of French and American oak best) deliver comprehensive flavor and a richer texture to the red, and white wine. Dub has a vanilla aroma and trastové and increasingly are used in a variety of cheaper forms (oak chips, planks hanging in stainless steel tanks), to impart a rectilinear oak flavor cheaper wines. There is nothing wrong, assuming, that you hold in your hand a glass of wine, rather than oak fluid, that remotely resembles wine. Oak in the form of precious barrels sometimes used recklessly ambitious, but insufficiently qualified or experienced winemakers. If the wine lacks concentrated fruitiness and acidity and tannins, Oak drown out all the flavor components of the young wine will prevail even after, What fruity taste and other colors fade.
Body
After assessing all the flavor components and structure of the wines and their mutual relationship, you should focus on the feel of the extract. The wine is light, medium-bodied, or full? The body of the wine determines, inter alia, mainly alcohol. He has a sweet taste and a high quantity of fire until slightly spicy conclusion. Like anything else, and alcohol should be in harmony with the other components. Too alcoholic wine will be hard and hot and will lack the ability refreshing.
Serenity
Uniformity is essentially a question of quality – the greater harmony between sugars, acids, tannins and alcohol, the wine is better. Nevertheless, the balance must be assessed in relation to the style of wine. Sancerrské wine should have particularly high acid content, while Condrieu and other wine varieties Viognier not, as it develops its typical Viognier varietal character only if, that the grapes were ripe acidity and relatively low. Red Burgundy should excel tannins such as red Bordeaux same quality and age. Similarly, Californian pinot noir from Santa Barbara County would not have such amount of tannins as cabernet sauvignon from the same grade and quality, vyrobený v Howell Mountain severně od Santa Barbary v Napa Country.
Conclusion
Eventually, if you have wine sent down into either the neck, or to the nearest spittoon, feel the taste, which leaves in the mouth. it is clean, pleasant, balanced and persists? If wears off in a few seconds, You have tasted simple, ordinary wine. But if it persists for about thirty seconds, you probably have a glass of something special.
Zdoj: www.encyklopedie-vina.cz
- Vilém Topolanský Pavlov
- Ilias Pavlov
- Abrle Biovíno Pavlov
- Zidek Popice
- Frederick Hustopeče
- wine Rakvice
- New Winery Drnholec
- Bíza Čejkovice
- Kadlec Vrbice
- Wissmann Poysdorf
- Blue Winery Mutenice
- Horak Vrbice
- Mikulica Pavlovice
- Hort Znojmo
- strike Nemcicky
- Croy Tvrdonice
- Tomčala Kobylí
- Hradil Čejkovice
- Valihrach Krumvíř
- Padalík Bořetice
- Jozef Kmeťo Modra
- Šlancar Boleradice
- Sedláček Kurdějov
- Kolby Pouzdřany
- Skoupil Great Bílovice
- Viticultural courtyard Nemcicky
- Haban Cellars Great Bílovice
- Rusnak Kobylí
- Lůbal Kobylí
- Tansberk Mikulov
- Reva Rakvice
- Patria Kobylí
- Hustopečská mandlovice
- Mandlovice from counselors
- Fortified wines Košulič Hustopeče
- Prchal Hustopeče
- Urban Wine Hustopeče
- Sekty Bohemia
- grape must
- Mead
- straw wines

Novelty!
Sending cask wine 1,5l PET
- Pálava 199,-
- Sylvaner 99,-
- Pinot Gris 99,-
- Pinot Noir rosé 99,-
- blue portugal 99,-
The price is added PET bottle 8,- CZK, and postage and packing.

- Opening hours
Mo - Fri: 15:00-19:00
So-I: In the absence of open on phone. order 606 808 805
Josef Stroh
Smetana 89/9
693 01 Hustopeče
TECH ICAL: 744 97 073
tel: 606 808 805
www.vinomistr.cz
info@vinomystr.cz
Josef straw per od 18.4. 2007 register of the Licensing Office
Municipality of Hustopeče under registration number: 370403-497768.